⇰ PROCESS :-
A process can be thought of as a program in execution. Means when any program is executed it becomes process. A processwill need certain resources such as CPU time , memory, files and I/O devices to complete its task. These resources are allocated to the process either when it is created or at the time of execution.
A process is the unit of work in most systems. A system consistes of a collection of processes. All these processes may execute concurrently. Traditionally a process contained only a single thread. Most modern operating ststems now supports processes that have multiple threads.
The operating system is responsible for several important works of process management as - the creation and deletion of process, the schrduling of process, communication and deadlock handling of process. Process is broudly divided into two types:-
i> System Process.
ii> User Process.
Early computers allowed only one program be executed at a time. This program had complete control of system and has access to all the system's resources. In a modern time-sharing systems a procee is the unit of work. Process is sometimes known as Text section. A process generally also includes the process stack, which contains tempeory data; data section; heap etc.
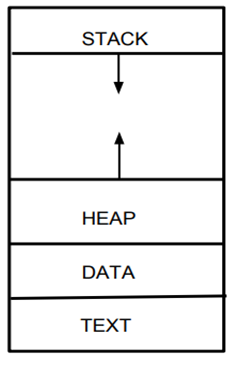
Stack :- The Stack contains temporary data such as parameters of function, returns address, and variables which are locally declared.
Heap Section :- This section of process stores dynamically allocated memory to process during its run time.
Data Section :- This section of process contains the global variables.
Data Section :- This section of process contains the global variables.
Text Section :-This section of process stores the current activity represented by the value of the Program Counter.
A program becomes a process when an ececutable file is loaded into memory. During the course of execution, a process may create several new processes. The creating process is called parent, and the new processes bare called children of that process. Most O/S identify processes according to a unique process identifiers (Pid), which is typically an integer number. The Pid provides a unique value for each procss in the system.
⇰ PROCESS STATE:-
As a process executes, it changes its state. The state of a process is defined in part by the current activity of that process. The states of process are mainly of 5 types :-
i> New.
ii> Ready.
iii> Running.
iv> Waiting.
v>Terminated.
i> New :- In this state of process, the creation of process of held.
ii> Ready :- In this state of process, the newly created process is waiting to be assigned to processor in ready queue.
iii> Running :- In this state of process, the instructions are being ececuted.
iv> Waiting :- In this state of process, the process id waiting for some event to occur such as I/O completion or reception of single.
v> Terminated :- In this state of process has finished executed.

⇰ PROCESS CONTROL BLOCK :-
Each process is represented in Operating System by process control block. Process control block is also called task control block because we know that process is also called task. As PCB contained with a specific process.
These informations are as follows :-
i> Process state:- It shows the state of process. It may be new, ready, running, waiting etc.
ii> Process Counter :- It indicates the address of next intruction to be executeted for this process.
iii> CPU-Scheduling information :- This information includes a process priority and many information.
iv> Memory management information :- This information may includes value of base and limit register and page table or segment table.
v> Accounting Information :- This information inclues the amount of CPU used, account number, time limit, process number and so on.
vi> I/O status information :- This information encludes the list of I/O device allocated to the process.

Comments
Post a Comment
Please comment.