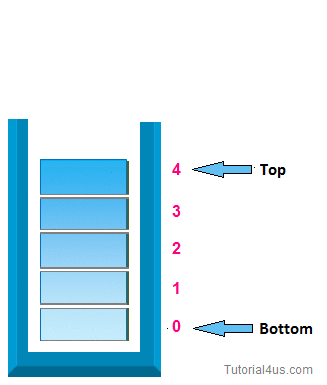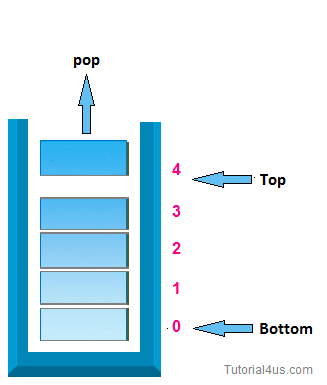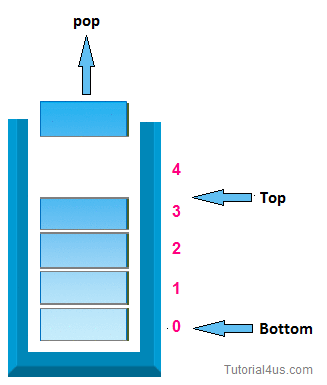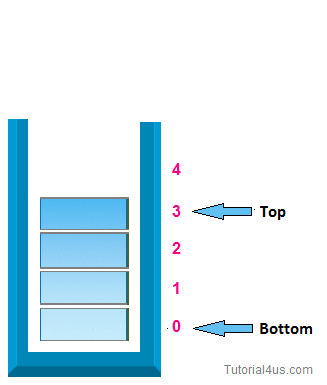
Stack
A Stack is an ordered collection of items where the addition of items and the removal of existing items always takes place at the same end. This end is commonly referred to as the “top".
* working method of stack :-
i> Initially top=-1
ii> By increasing top pointer we can insert element in the stack.
iii> when top=size of stack-1 then stack is full.
iv> By decreasing the top pointer we can remove the element from stack.
v> when top=-1 then the stack is empty.
 |
| figure shows run time stack |
* The fundamental operations which are possible on a stack are:-
1. push operation (insertion).
2. pop operation (deletion).
3. peep opetation(extract information).
4. update operation (change value at any position).
1. push operation:-
In case of stack Insertion of any item in stack is called push. In stack any item is inserted from top of the stack, When you insert any item in stack top will be increased by 1.
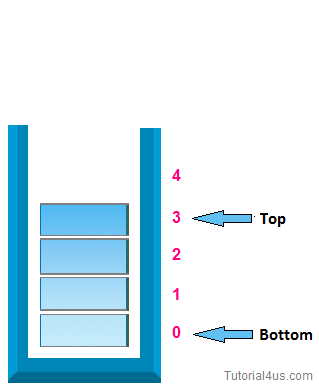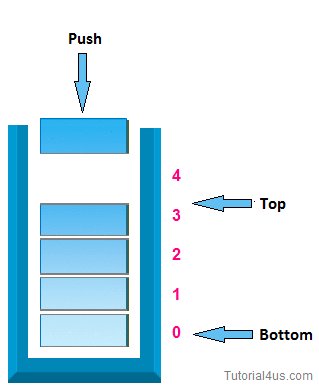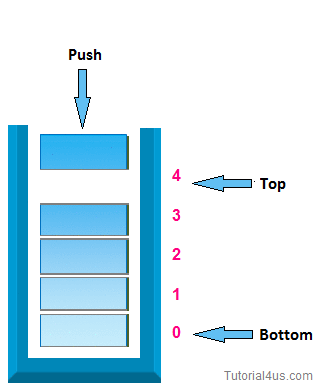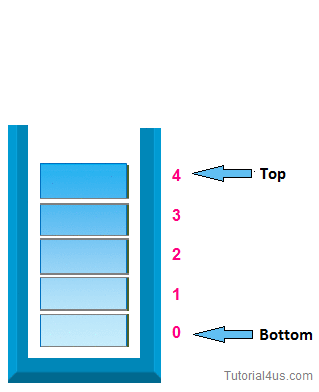
* Algorithm for insertion (push operation):-
Step1: [Check for stack overflow]
If top>= size of stack then
output:- " stack is overflow " and exit.
Step 2: [Incriment the pointer value by 1 ]
top=top+1
Step 3: [perform the insertion operation ]
S[top] = value. (here S is array name)
step 4: Exit.
2. pop operation:-
In case of stack deletion of any item from stack is called pop. In any item is delete from top of the stack, When you delete any item from stack top will be decreased by 1.
* Algorithm for deletion (pop operation ):-
Step 1: [Check for stack underflow]
If top=0 then
output:- "Stack is underflow " and exit.
step 2: [Removing the top valve ]
value = S[top].
step 3: [decrementing the pointer value by 1 ]
top = top-1
Step 4: [Return the formal information os the stack ]
return ( value )
3. peep operation :-
If we are interested about any information stored at any locatoin in a stack, finding that information is known as peep operation.
In this operation we simply move the pointer in the desired location fetch the information associated with that location.
* Algorithm for peep operation:-
Step 1: [check for stack underflow ]
if top-i +1<= 0 then (here i is the position which have to extract)
output:- "stack is underflow " and exit.
Step 2: [return the ith element from the top of stack]
return (S[top-i +1])
4. update operation:-
Update operation is required when the containt of same location in a stack is to be changed. If we want to update value at ith position in a stack S , we move top pointer to the ith loction from the top of the stack and input new value of that location.
* Algorithm for update opertaion:-
Step 1: If top-i +1<= 0 then
output:- "stack is underflow " and exit.
Step 2: [Change the element ]
S[top-i+1] = value.

Bohot achha h ..keep it up
ReplyDeleteVery helpful
ReplyDelete