An operating system is a system software which acts as an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which a user can execute programs in a convenient and efficient manner. Since an operating system is large and complex, it must be created piece by piece. Each of these pieces should be a well-delineated portion of the system, with carefully defined inputs, outputs, and functions. Ex:- Unix, Linux, MS Dos, macOS, windows, android etc.

* Important functions of an operating System:-

1.Memory Management:- The operating system manages the Primary Memory or Main Memory. An operating system keeps tracks of primary memory, i.e., which bytes of memory are used by which user program. In multi programming, the OS decides the order in which process are granted access to memory, and for how long. It Allocates the memory to a process when the process requests it and deallocates the memory when the process has terminated or is performing an I/O operation.

* Important functions of an operating System:-
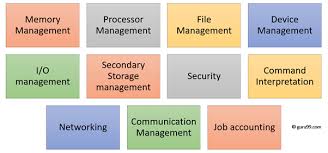
1> Memory Management.
2> Processor Management.
3> Device Management.
4> File Management.
5> Security providing.
6> Job accounting.
7> Control over system performance.
8> Error detection.
9> Coordination between other softwares.

1.Memory Management:- The operating system manages the Primary Memory or Main Memory. An operating system keeps tracks of primary memory, i.e., which bytes of memory are used by which user program. In multi programming, the OS decides the order in which process are granted access to memory, and for how long. It Allocates the memory to a process when the process requests it and deallocates the memory when the process has terminated or is performing an I/O operation.
2. Processor Management:- In a multi programming environment, the OS decides the order in which processes have access to the processor, and how much processing time each process has. This function of OS is called process scheduling. Also keeps tracks of the status of processes.
3. Device Management:- An OS manages device communication via their respective drivers. It keeps tracks of all devices connected to system.. Decides which process gets access to a certain device and for how long. Allocates devices in an effective and efficient way. Deallocates devices when they are no longer required.
4. File Management:- A file system is organized into directories for efficient or easy navigation and usage. An Operating System keeps track of where information is stored, user access settings and status of every file and more.These facilities are collectively known as the file system.
5. Security Providing:- The operating system uses password protection to protect user data and similar other techniques. it also prevents unauthorized access to programs and user data.
6. Job accounting:- Operating system Keeps track of time and resources used by various tasks and users, this information can be used to track resource usage for a particular user or group of users.
7. Control over system performance:- Monitors overall system health to help improve performance. Records the response time between service requests and system response to have a complete view of the system health. This can help improve performance by providing important information.needed to troubleshoot problems.
8. Error detecting :- Operating system constantly monitors the system to detect errors and avoid the malfunctioning of computer system.
9. Coordination between other softwares:- Operating systems also coordinate and assign interpreters, compilers, assemblers and other software to the various users of the computer systems.

This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteNyc bro
ReplyDelete