LINKED LIST
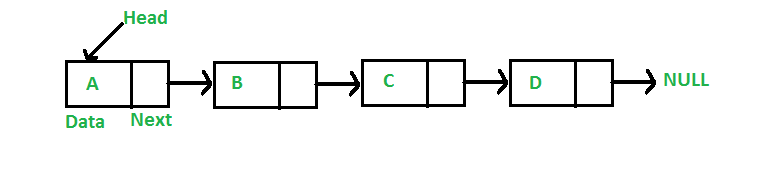
A linked list is non-premitive data structure. A linked list is a way to store a collection of elements. Like an array these can be character or integers. Each element in a linked list is stored in the form of a node. And a node is a collection of two sub-elements or parts , information or data part and another is address part . A linked list is formed when many such nodes are linked together to form a chain. Each node points to the next node present in the order. The first node is always used as a reference to traverse the list and is called Start or head and the last node points to NULL.

Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have some limitations as the size of the arrays is fixed: So we must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to the upper limit irrespective of the usage. Inserting a new element in an array of elements is expensive, because room has to be created for the new elements and to create room existing elements have to shifted . Random access is not allowed. We have to access elements sequentially starting from the first node.
To overcome these limitation of array the concept of linked list is introduced. Following are the basic operations supported by a list.
Insertion − Adds an element at the beginning of the list.
Deletion − Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
Display − Displays the complete list.
Search − Searches an element using the given key.
Delete − Deletes an element using the given key.
Traverse - Move from first node to desired node.
There are three common types of Linked List :-
Singly Linked list.
Doubly Linked list.
Circular Linked list.
Singly linked list is commonly used linked list , which is well explained above. Now we can traverse forward in singly linked list but sometimes it is required to travel the list in either the direction which is possible in singly linked list. To overcome this limitation of singly linked list ,doubly linked list is introduced. This type of list uses two pointers for predecessor and successor of each node.the link denoting the predecessor is called 'left link' and that denotes the successor is called 'right link' .
Hence a node have three fields. Out of which one is information field and two are address fields of previous and next node. So we use two pointer variables and one normal variable.
Now Circular linked list is a linked list where all nodes are connected to form a circle. There is no NULL at the end. A circular linked list can be a singly circular linked list or doubly circular linked list. Any node can be a starting point. We can traverse the whole list by starting from any point. We don’t need to maintain two pointers for front and rear if we use circular linked list. We can maintain a pointer to the last inserted node and front can always be obtained as next of last.

Well done Priy Ranjan
ReplyDelete