⇰ TREE TRAVERSAL :-
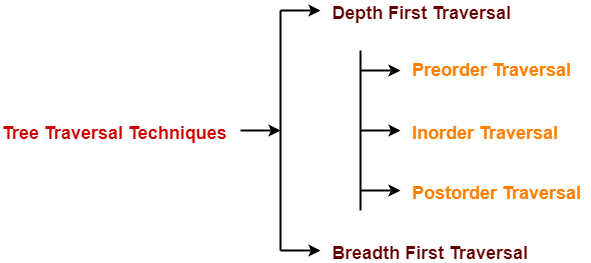
Tree Traversal refers to the process of visiting each node in a tree data structure exactly once. You might for instance want to add all the values in the tree or find the largest one. For all these operations, you will need to visit each node of the tree atleast and exectly once. Linear data structures like arrays, stacks, queues and linked list have only one logical way to read the data. But a hierarchical data structure like a tree can be traversed in different ways. Following are the generally used Techniques for traversing trees :- i>Breadth First Traverse.
ii> Depth First Traverse.
ii> Depth First Traverse.
i > Breadth First Traverse :- Breadth First Traverse of a tree is technique of printing all the nodes of a tree level by level. It is also called as Level Order Traversal.
Here if we traverse in above tree by breadth first treverse technique the traversal will be on level wise as in the order :- 1 2 3 4 5 6.
ii > Depth First Traverse :- Depth-first traverse is a method of tree traversal . In Depth First traverse we go as deep as possible down one path before backing up and trying a different one.
Following three traversal techniques fall under Depth First Traversal :-
∗ Preorder Traversal.
∗ Inorder Traversal.∗ Postorder Traversal.
Algorithm :-

2. Visit the root.
2.Traverse the right sub tree.

Algorithm :-
2. Visit the root.
2.Traverse the right sub tree.
∗ Preorder Traversal :- In this technique first of all we process the root of the binary tree. Then we traverse the left sub tree in pre order. After complition of left sub tree , then we take over right sub tree and procee all the nodes in pre order.
1.Visit the root.
2.Traverse the left sub tree.
3.Traverse the right sub tree.
Root → Left → Right
∗ Inorder Traversal :- In this technique first of all we process the left subtree in inorder. Then process the root and at the last we process the rioght sub tree in inorder
Algorithm :-
1. Traverse the left sub tree.
3. Traverse the right sub tree.
Left → Root → Right

Here if we traverse in above tree by Inorder treverse technique the traversal will be as in the order :- 1 5 6 7 10 12 14 16.
∗ Postorder Traversal :- In this technique first of all we process the left subtree in inorder. Then process right subtree in postorder and at the last treverse to root.
Algorithm :-
1.Traverse the left sub tree.
3.Visit the root.
Left → Right → Root
More Example :-
FOR BASIC CONCEPT OF TREE DATA STRUCTURE GO THROUGH THIS LINK :- https://priypurnea.blogspot.com/2020/04/basic-concept-of-trees-and-its-type-in.html
FOR TYPE OF BINARY TREE STRUCTURE GO THROUGH THIS LINK :- https://priypurnea.blogspot.com/2020/04/types-of-binary-tree.html
Share, Follow and please comment if you find anything incorrect, or to share more information about the topic discussed above.

Comments
Post a Comment
Please comment.